Q&A
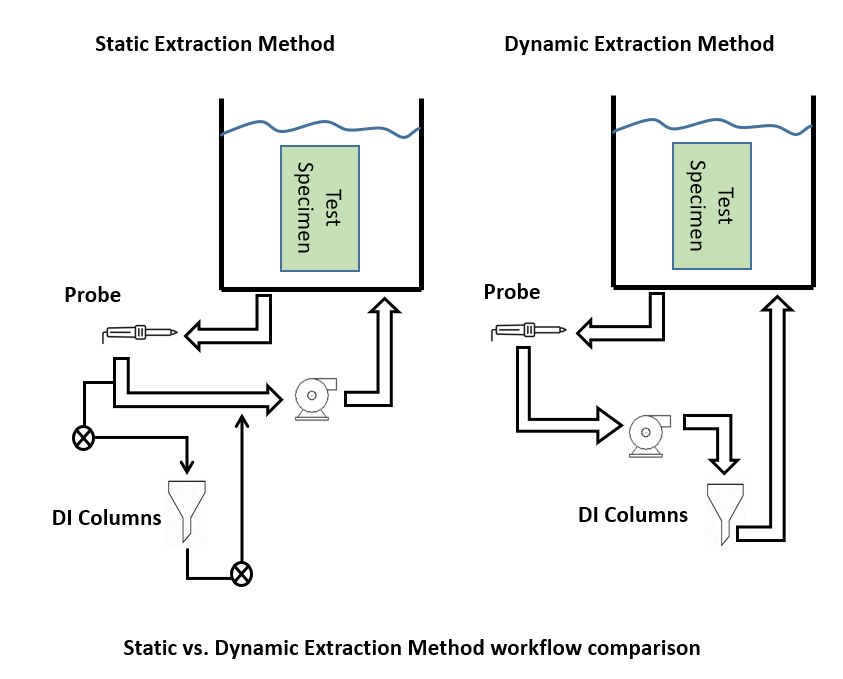
Static testing involves dissolving contaminants on the test specimen's surface into a solution and measuring the resistivity of the solution. This final resistance value is then compared to NaCl of the same resistance, yielding a value equivalent to the NaCl concentration. Static testing requires purification of the extraction solution before testing to ensure it meets the specified resistance requirement, and the extraction solution is not purified during the test.
The dynamic test method is a continuous test. In the test tank, the extraction solution flows over the surface of the test specimen to dissolve the contaminants (similar to the static system), and then flows into the pipeline. The solution passes through the electrode probe, and the probe continuously collects resistivity data from the extraction solution, which is then statistically integrated by the software running on the computer. The solution is then introduced into the ion exchange column by the motor for purification, and finally flows back to the test tank, completing the circulation of the extraction solution. Compared with static testing, the solution extraction solution can show higher solubility and ionization. This is because the solution recirculated after the test is pure. The increment of the contaminant reading is the accumulation or integration over a period. The final contaminant value is compared with the standard to give a value equivalent to the NaCl concentration.
Dynamic testing is generally more accurate than static testing. This is because contaminants are more strongly ionized in pure solutions than in the more polluted or saturated solutions used in static testing. Using an analogy to daily life, static testing is like taking a bath, while dynamic testing is like showering. While both serve the same cleaning purpose, showering provides a more thorough cleansing effect.